







Sessions
Land Seismic Acquisition Technology
operations and 3D acquisition geometries Hi-channel count single sensor (point receiver) operations in a variety of different terrains and environments Typical 3D land acquisition geometries limitations attributes and metrics. single sensor and single source acquisition vs arrays consequences for data processing characteristics of ambient and coherent noise coherent noise sampling and filtering
Land Seismic Acquisition Technology
Simultaneous source, high-productivity vibroseis Broadband Wireless nodal systems Cost benefit of simultaneous source acquisition, different methodologies, data quality and operations efficiency data processing. Broadband data usage on resolution. low frequencies: how they can be obtained in the field. Nodal systems impact on acquisition operations. Analyse operational efficiency and its parameters.
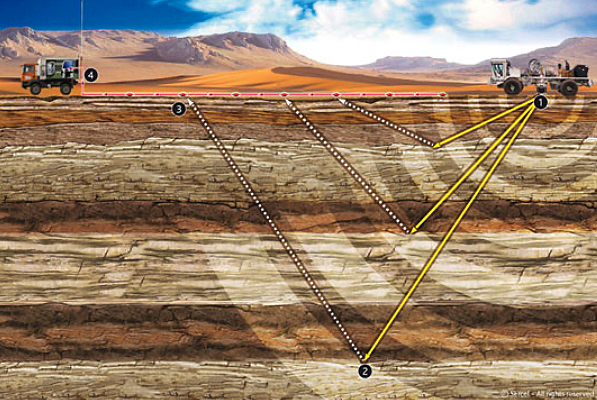
Survey Design Basics
Survey design basics 1D earth model
- offset/angle limits,
- muting,
- bin size,
- fold,
- migration aperture
OMNI:
- array response
- resolution analysis
- maximum offset
- migration aperture
Designing a 3D geometry
Survey design impact on imaging 3D acquisition geometry, ray-tracing & illumination translate basic survey design parameters and objectives into a 3D acquisition geometry choose between te different geometry options. relationship between acquisition geometry and modern time and depth imaging workflows
New processing technology
noise attenuation, surface wave inversion, irregular geometries, interpolation and compressive sensing, demultiple Survey design impact on inversion (AVO, pre-stack, AVOAz) noise attenuation, surface wave inversion and demultiple. Noise attenuation technology non-uniform survey layout New interpolation and compressive sensing technology impact on survey design. AVO, pre-stack inversion and AVOAz (fractures & stress) place on survey design.