
Sessions
Introduction
Course overview. Seismic applications at the different scales of oil and gas E&P
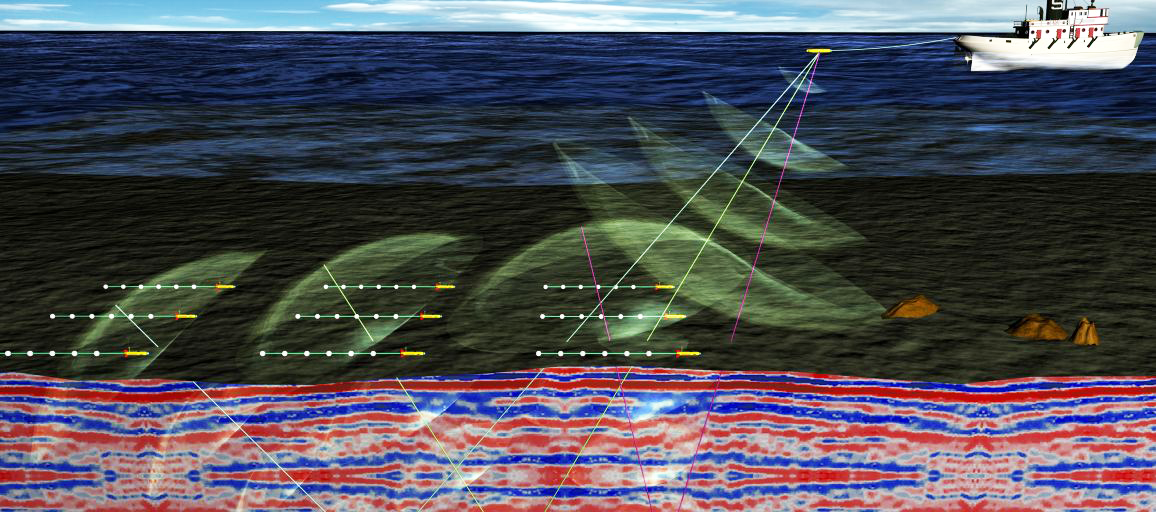
3-D seismic acquisition
Fundamentals of acoustic waves propagation
Characteristics and limitations of acquisition systems in marine and land domains; consequences on interpretation
3-D seismic processing
Description of standard processing sequence
Migrations: post-stack and pre-stack, in time and depth domains. Interpreter’s implication. Anisotropy.
Essential first step well tie in calibration
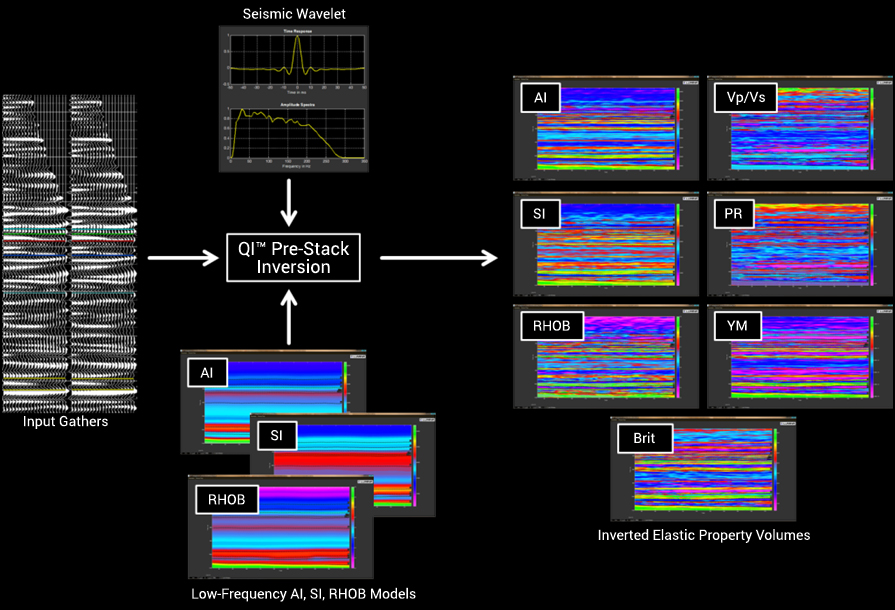
Initial review of footprints, wavelet, resolution Seismic tie to well data in time and in depth domains. Check- shots, synthetic seismograms, VSP. Inversion Other calibration means
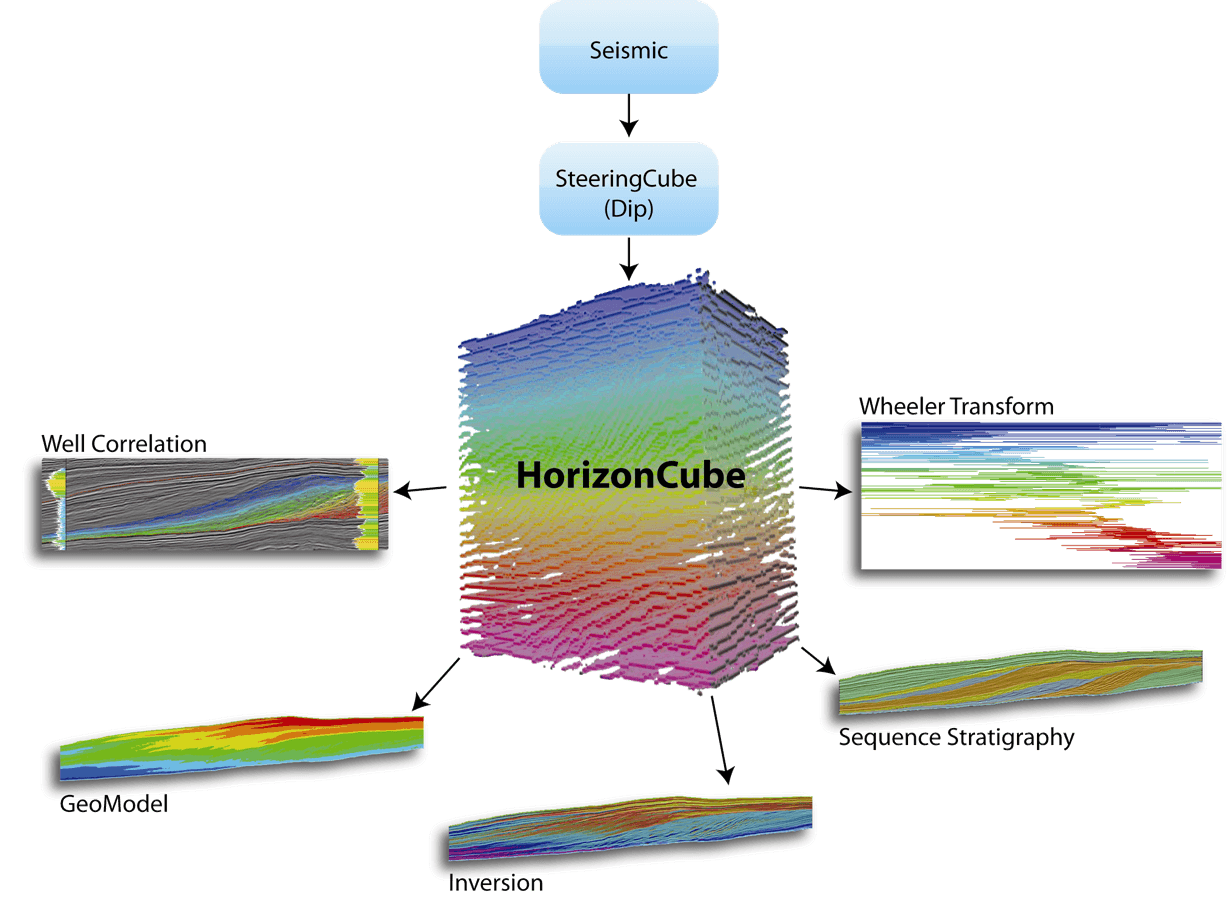
Horizon and faults pickings
Techniques and tools for horizons and faults Review and applications of various attributes Pitfalls Field examples and hands-on exercises
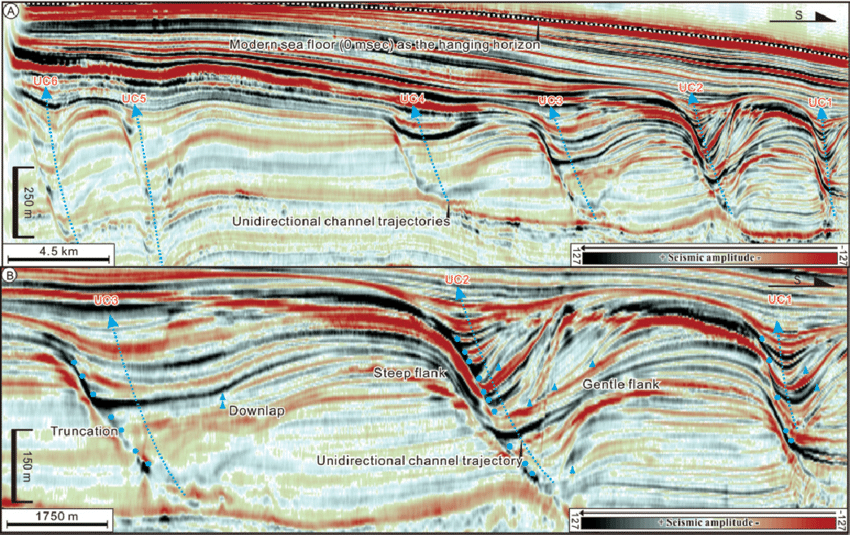
Structural and stratigraphic interpretation
Structural interpretation, with emphasis on compressive and gravity tectonics Seismic stratigraphy, with emphasis on deltaic environment Specific environments: carbonates, salt tectonics
Depths conversion gridding and mapping
Velocity and depth conversion: choice of model Gridding: use of kriging method. Seismic map to well tie Mapping
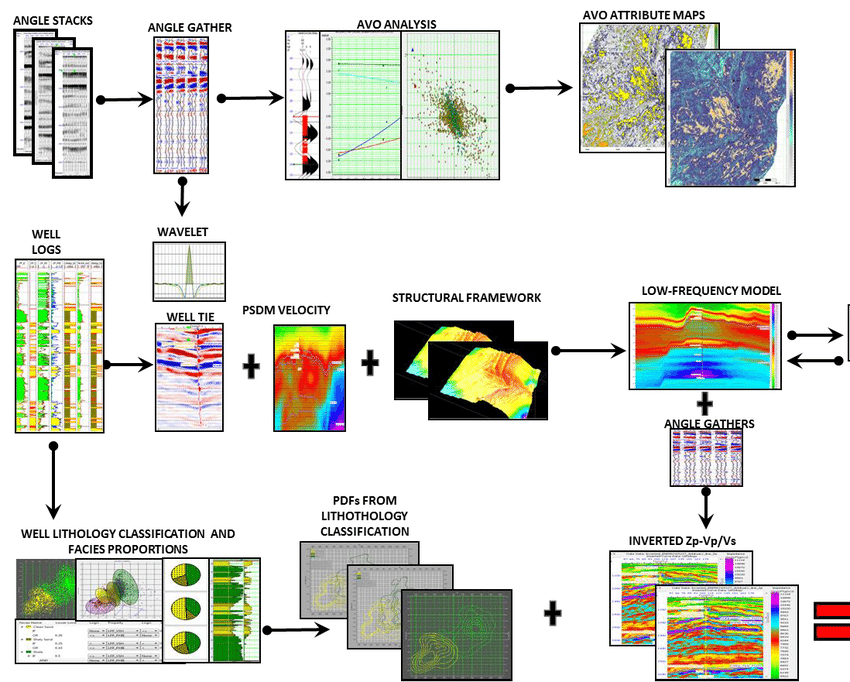
Direct hydrocarbon indicators (DHI’s)
Fluid effects on full stack cubes: on polarity and amplitudes Fluid effects versus angle (AVO): principle and applications Tools to be used Pitfalls. Review of examples. Quiz
3-D interpretation for reservoir management
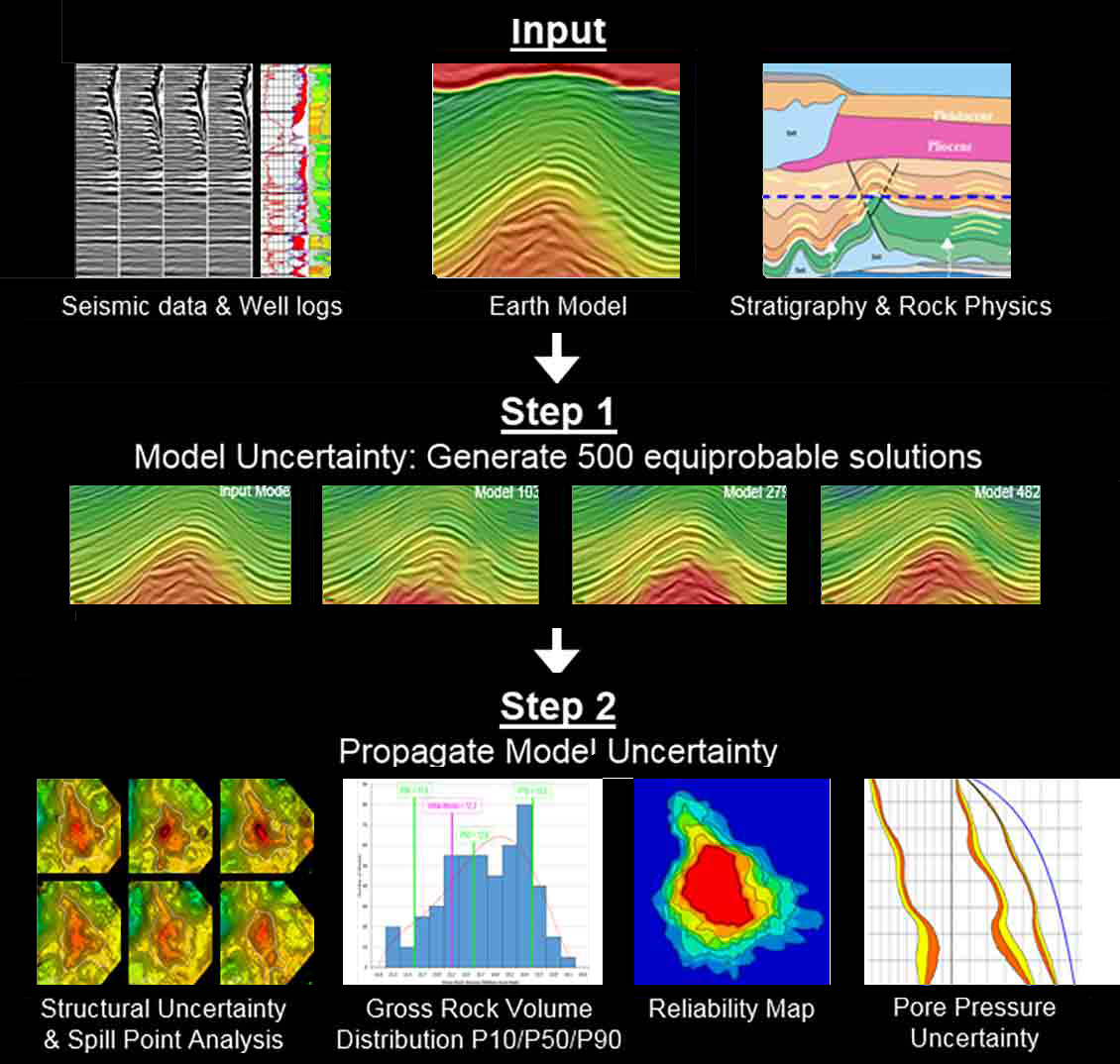
Drilling: geo-hazards, abnormal pressures prediction. Appraisal: delineation, reservoir modeling Development: geosteering, time-lapse seismic monitoring
Other methods
3 components method. Review of some application cases 4D seismic Passive seismic for unconventional resources.
Case studies around the world
Review of 3D and 4D successful applications worldwide Lessons learnt by selected historical failure cases Conclusions Quiz